In this blog , I will explain how to boost your MySQL performance more than 100x times faster without the help of a DB expert. Most importantly, it is very useful if your project has been developing without a DB performance expert. Also, if your DB is serving live traffic and frequently triggers production issues such as deadlock, Query locking, Replication lagging, Poor Query response & DB server hanging with High CPU usage, high RAM, high Disk IO usage problems which are slow down DB server performance. In fact, these issues cause a DB service outage at pick traffic time.
What is the Root Cause of these issues?
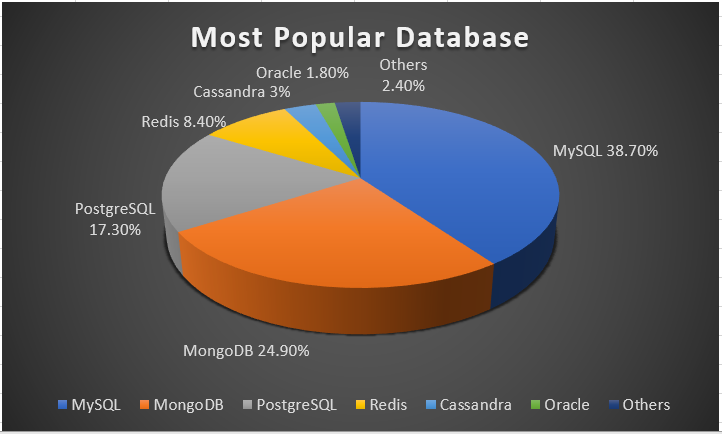
One of the main reason is bad indexing. Generally, After developing SQL queries for your project those must optimize for getting the best performance. But, there are high chances to make mistakes in the Query optimization area and missing the optimal indexes (good index) if the query optimized done by nonprofessional (for ex, application developers or DBA engineers). It supposed to be done by a DB performance expert or DB architect. But It is happening only in industry-leading companies such as YouTube, Facebook, linked in, twitter.
Query Optimization:
Query Optimization is nothing but selecting a good index for your queries. In fact, it is difficult to select a good index out of N!*(N-1)+N possible indexes. Here N is no.of columns in WHERE, GROUP BY and ORDER BY clauses. In the first place, it needs to create a good index for getting the best performance whenever developing the DB queries. Most impatiently, It should choose the right columns with the right order in an index based on the index behavior and their design.
Indexes are very sensitive their behavior will be change based on filter types, logical operator between filter conditions, columns cardinality, apply functions on the filter column, arithmetic operations with filter columns, JOIN condition, Grouping function, GROUP BY clause columns and ORDER BY clause columns order.
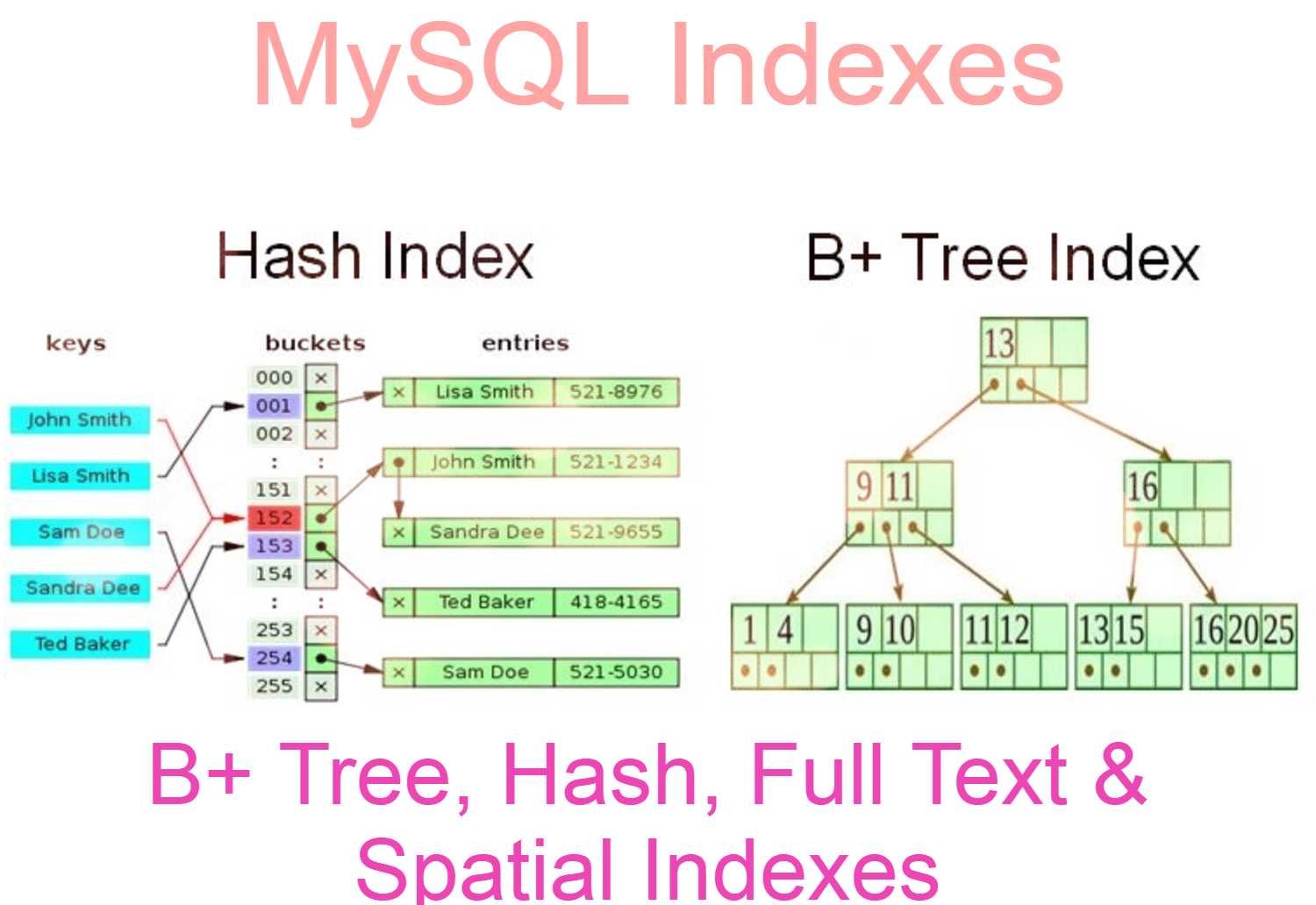
As a reality, It is not difficult to lean but daily it needs to spend more time to become an expert. Also, it needs regular practice. First, you need to learn the MySQL EXPLAIN plain. Generally, It shows the optimizer execution plan of the query. It is easy to identify whether the query is using a good index or not. Second, you need to learn B tree, hash, full-text indexes architecture and their behavior. As an example, You need to understand how the indexes filter rows with help of where clause filters and filter types. In addition, do some experiments on test DB and take DB performance expert’s help. Also, there are some tools available for Query Optimization. Use them until you become an expert in case of DB performance expert’s unavailability.
In many cases, real-time queries are complex and there is a high chance to do mistakes without the help of DB performance experts or tools. In my view, it is not a good approach to optimize real-time queries with application team or DBA team. The following query is one of the real-time queries.
SELECT smartmysql_tasks.*,smartsql_groups.*
FROM
smartmysql_tasks_bak smartmysql_tasks
JOIN smartmysql_task_states
JOIN smartsql_groups
WHERE
((smartmysql_task_states.ticket_id = smartmysql_tasks.id)
AND (smartmysql_tasks.status = 2)
AND (smartmysql_task_states.group_escalated = 0)
AND (smartmysql_tasks.deleted = 0)
AND (smartmysql_tasks.spam = 0)
AND (smartmysql_tasks.client_id = 178244)
AND (smartmysql_task_states.client_id = 178244)
AND (smartsql_groups.account_id = 178244 )
AND ((smartmysql_tasks.created_at + INTERVAL smartsql_groups.assign_time SECOND) <= '2017-11-07 02:58:25')
AND ISNULL(smartmysql_task_states.first_assigned_at)
AND (smartmysql_tasks.updated_at > '2017-09-07 02:58:25')
AND (smartsql_groups.id = smartmysql_tasks.group_id))
ORDER BY
smartmysql_tasks.id LIMIT 1000;How to Check your SQL Queries using optimal indexes?
However, MySQL saves how many rows scans and how many rows returns for a query in MySQL slow query log file and sys.statement_analysis view. In fact, if queries are scanning rows more than 120% of total return records then the queries don’t have good indexes/ optimal indexes.
Also, If your DB is serving live traffic and frequently triggers production issues such as deadlock, Query locking, Replication lagging, bad query response time, DB server hanging with High CPU usage, high RAM, high Disk IO usage problems which are slow down DB server performance indicates SQL queries don’t have optimal indexes.
How to Optimize MySQL Queries?
As for my knowledge, I will explain a simple, easy and efficient way to do MySQL Query optimization. It speeds up your SQL Query performance more than 100X using one of my favorite tools called the SmartWorkbench. It is a MySQL GUI tool having many advanced features. Query Optimization feature is one of them and only this tool has a Query optimization feature. However, It is simple, easy and anyone can optimize SQL queries without DB performance experts help. Develops, Programmers & DBAs can optimize their SQL queries while developing them using SmartWorkbench. Also, It has the option to optimize SQL queries from MySQL’s slow query log file, or Performance schema’s metadata tables.
However, It is easy to identify such problems using SmartWorkbnech. It can trigger a warning after you have developed the SQL query ends with a semicolon(;). In addition, The tool automatically analyzes the query and gives a warning if the query doesn’t have an optimal index. In another possibility, if it goes for a full table scan in the MySQL optimizer Query execution plan.
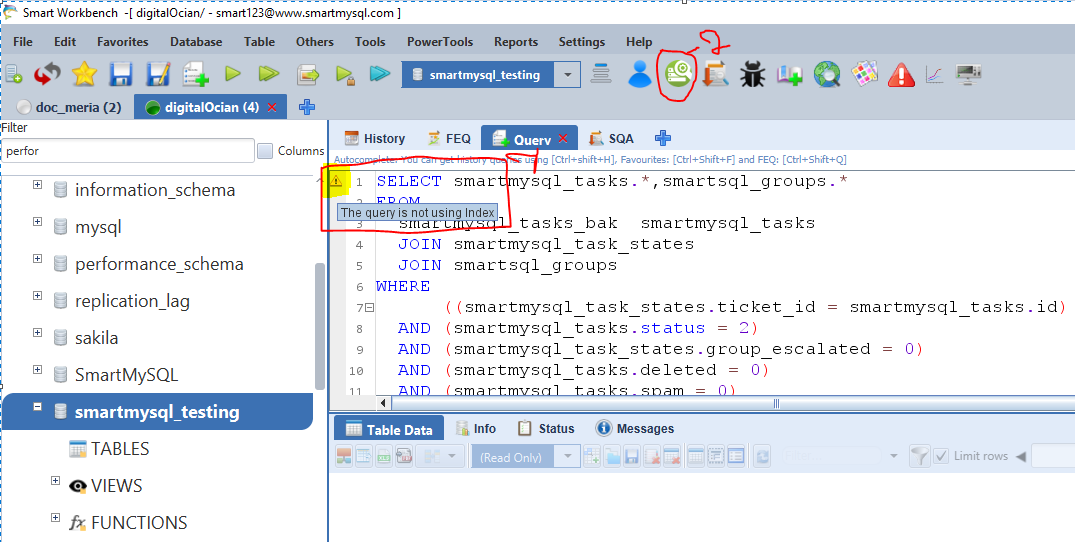

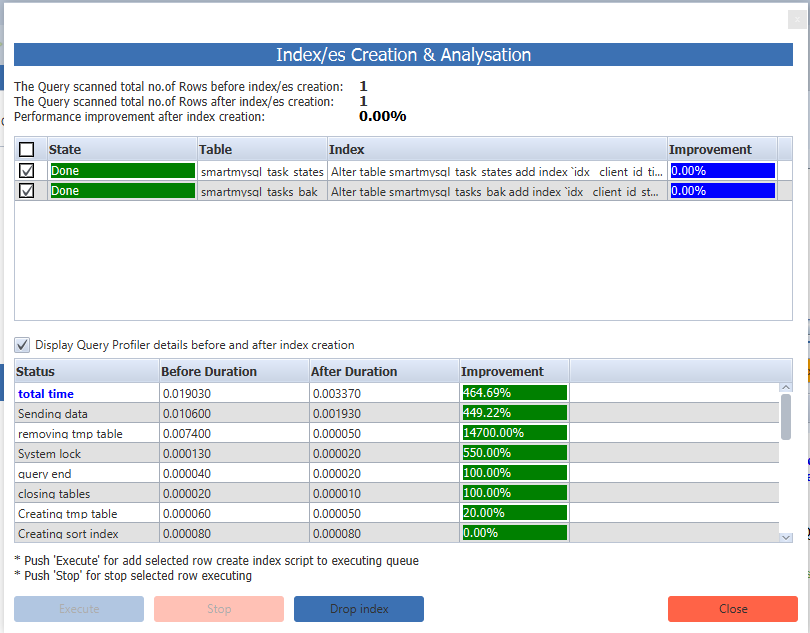
After that, If you click that warning icon(1) or Query Optimizer icon (2) Then it will open the Query Optimizer module.
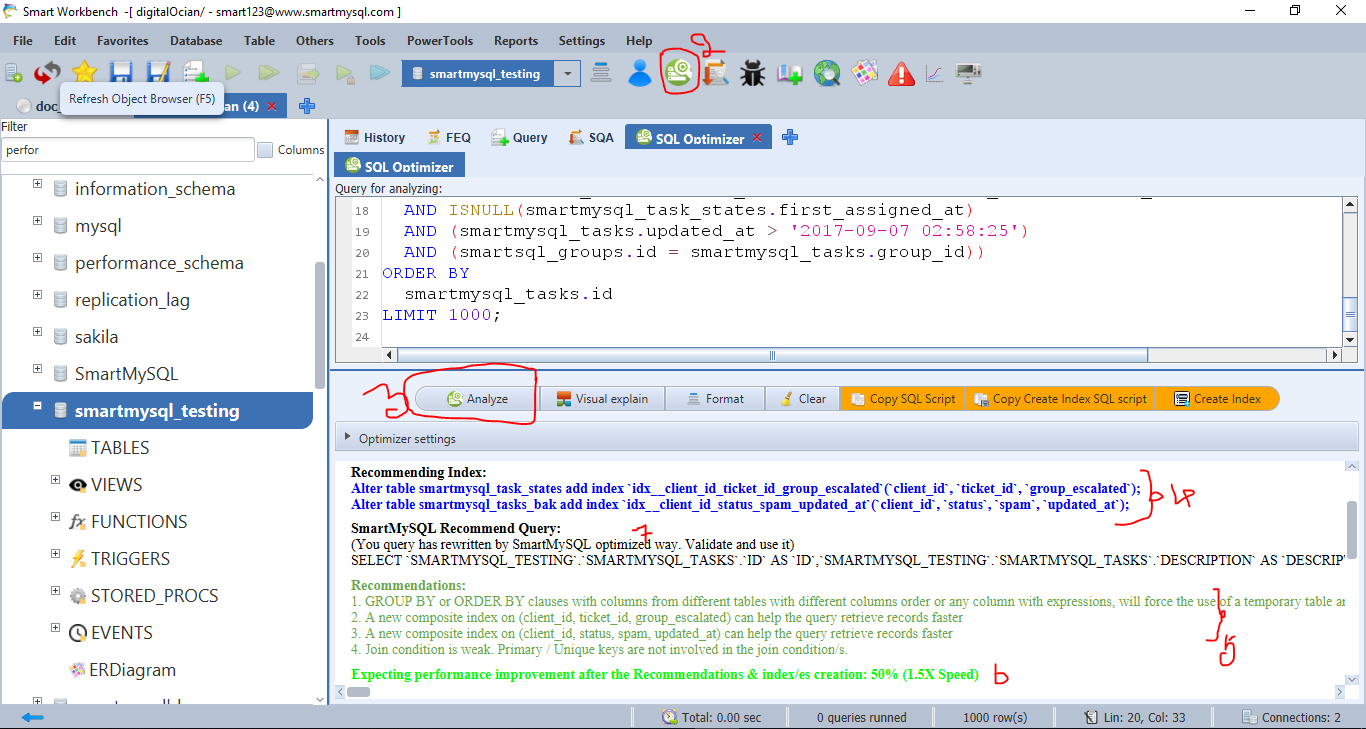

After that, Run the analyzer(3) button then it will recommend optimal indexes(4), Query rewrite recommendations(5,7) and expected performance improvement(6). After that, if you click the “Create Index” button then it will add recommended indexes. Also, provide a consolidated performance improvement report with all details such as percentage of improvement in scanning records, percentage of query execution time improvement for each state of query execution. In fact, It is very useful to identify significant performance improvement before and after Query optimization changes. Most of the cases, It has given more than 100X performance.

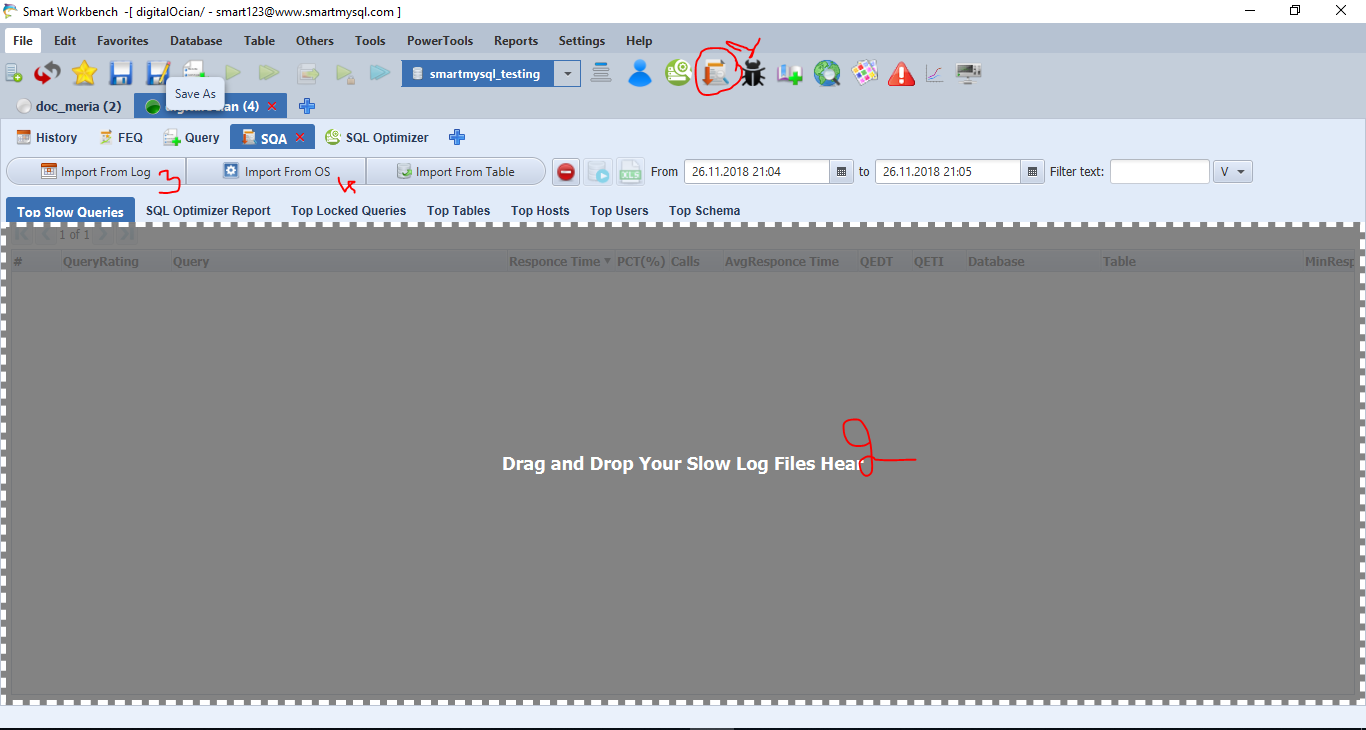
How to Optimize all slow queries in a MySQL server?
Moreover, there is an advanced feature called the Slow Query analyzer (1) in the SmartWorkbench tool. It can pull MySQL’s Slow Query log directly from MySQL server’s OS(4) if you save the DB server’s OS connection. Alternatively, It allows, you to upload your MySQL slow Query log files(3) or drag and drop files(2).

After that, It shows a consolidated report. It includes high frequency executed Queries, slow response queries, Queries execution time, lock time, total scanned records, total returned records, and Query ratting. It is highly useful and easily identifies problematic queries that are not optimized by DB performance experts. Most Importantly, the Query Optimizer module integrated with this report. I mean It can do Query optimization for all slow queries and provide optimal indexes for all of them at once. After implementation, You can observe significant overall DB performance. As a result, the application gives good responses to end-users.
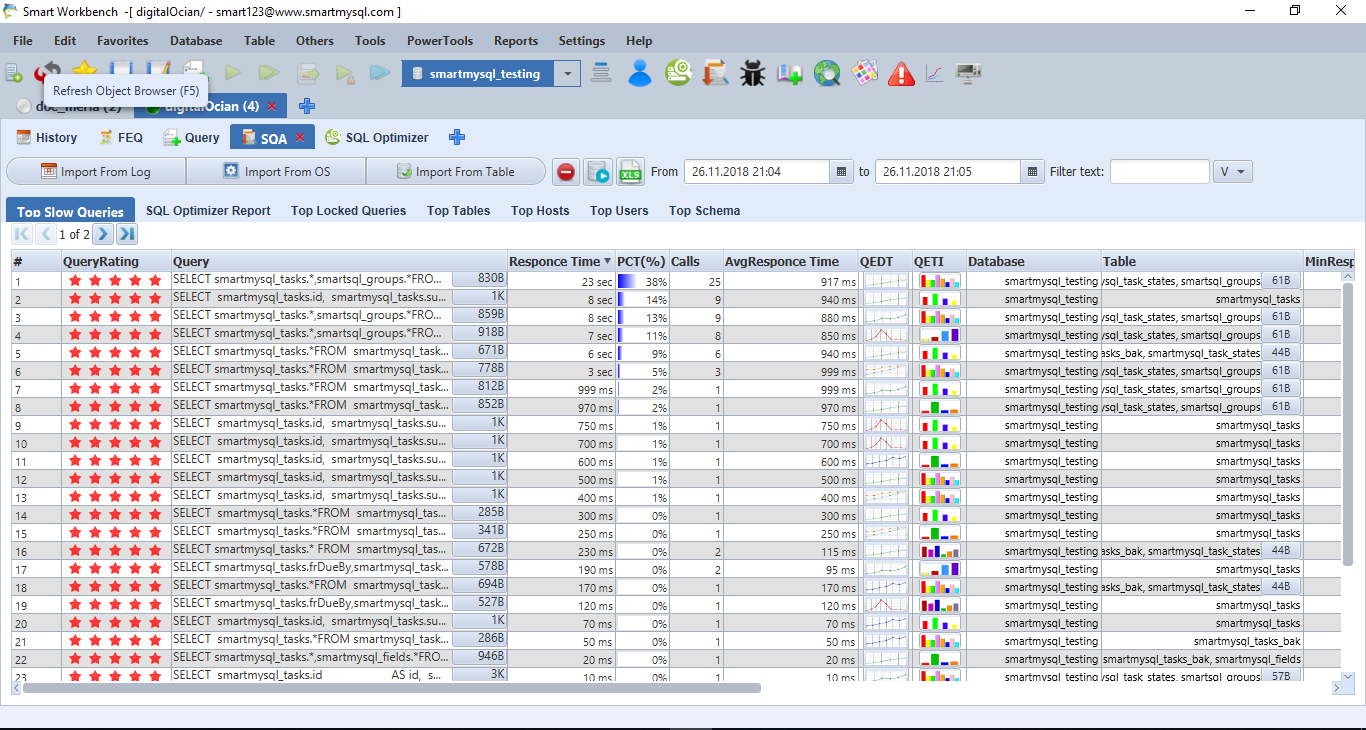

Query Rating: it calculates query ratting based on how many rows scanning and how many rows it returns. The red stars indicate the Query is needed query Optimization.
Details:
Query: It is a Query template
Response time: it is the total response time
Pct(): calculate query response percentage based on total response time
Avg Response Time: It is Avg response time
QEDT: Query Execution Date & Time Graph
QETI : Query Execution Time Interval Graph
And it has much other information such as min, max, stddev response time, Lock time, Rows sent and rows examined.
it will run the Query optimizer for each query template in the slow qerylog files. Also, it provides a list of recommended optimal indexes for all your slow queries.
What is the Optimal Index?
IN many cases, MySQL Optimizer uses only one index per table for filter records in most of the cases. In fact, there will be N!*(N-1) +N no.of indexes combinations that are available for the query. Here N is no.of unique columns in WHERE, GROUP BY and ORDER BY clauses. All columns belong to the same table and N >=1.
, there are high chances to make mistakes in the query optimization area and missing the optimal indexes if the query optimized done by nonprofessional. Generally, It supposed to be done by a DB performance expert or DB architect.
We must select columns for index based on index type and index’s behavior. There is only one index per table per query which can scan fewer records to return the result. In many cases, It will not scan more than 120% of return records. It is nothing but an Optimal index. In fact, there is very little probability to select the optimal index using shortcut /easy methods by nonprofessionals.
- If N=1 then 1+1!*(0) = 1+1*(0)=1 possible index
- If N=2 then 2+2!*(1) = 2+1*1*(1)= 4 possible Indexes
- If N=3 then 3+3!*(2) = 3+3*2*(2)=15 possible indexes
- If N=4 then 4+4!*(3) = 76 possible indexes
- If N=5 then 5+5!*(4) = 485 possible indexes.
- If N=6 then 6+6!*(5) = 3606 possible indexes.
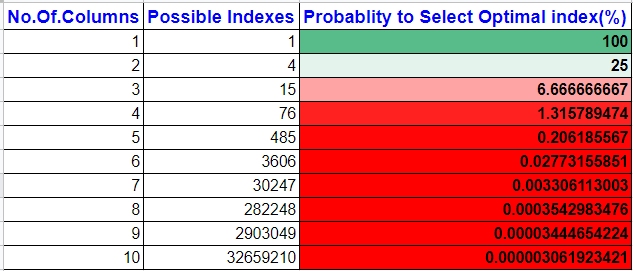

This table represents the probability of select optimal index based on the no.of column in WHERE, GROUP BY & ORDER BY clauses. In fact, It is gradually reducing the probability of selecting Optimal indexes if the no.of columns are increasing and it almost becomes zero if the query has 5 or more columns in WHERE, GROUP BY & ORDER BY clauses.
Examples:
The following Queries look almost similar only difference with the logical operator between where clause filter condition but index behavior is quite different from these queries, and we should create different indexes
Query A
Select * from EMP where Name='JOY' and DEPT='IT';
Query B
Select * from EMP where Name='JOY' or DEPT='IT';We have to select an index on (Name, DEPT) with the same order for Query A, but we should create individual indexes on (Name) and (DEPT) column for Query B because the “OR” logical operator is not favor of B tree indexes and MySQL convert query B with unions as below. After that, it needs individual indexes on each column to speed up the query execution time.
Query B
SELECT * from EMP where Name='JOY'
union
SELECT * from EMP where DEPT='IT';There are many factors and rules based on index type and behavior. We should follow all of them for getting the best performance for the query. Let us take another more example with three filter columns
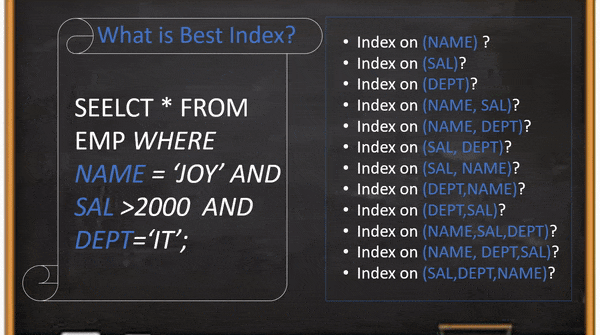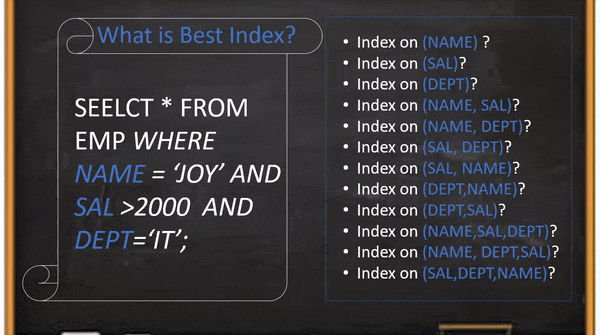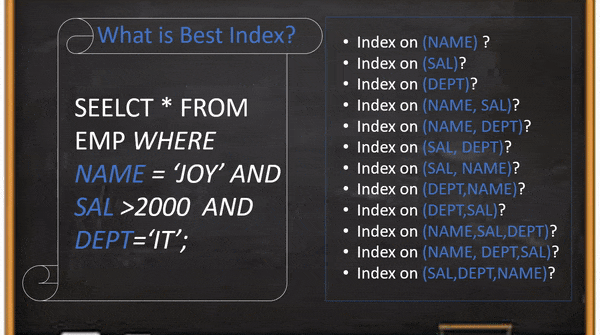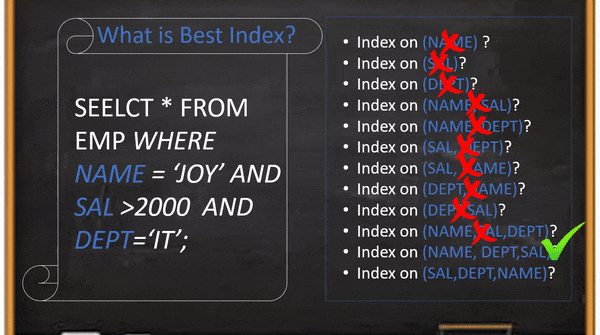

In this example, if the user creates an index on the “SAL” column and the table has more than 50% records salary greater than 2000 then the query will scan 50% records using an index on the “SAL” column to return the result set which is one or two records. It looks better than a full table scan query but It is not a good index for DB to scan your query 50% of total records for returning 2 records. Even it is not the optimal index if you create a composite index on the same order or reverse order. The root cause is the rang filter(SAL>2000) always should be the last position because index conditional push will not work after rang filter. And We have to select other columns and positions based on the column’s cardinality.
Those above examples are simple queries and easy to learn but in real-time the queries are complex and there is a high chance to do mistakes without the help of experts or tools. The following query is one of the real-time queries.
SELECT smartmysql_tasks.*,smartsql_groups.*
FROM
smartmysql_tasks_bak smartmysql_tasks
JOIN smartmysql_task_states
JOIN smartsql_groups
WHERE
((smartmysql_task_states.ticket_id = smartmysql_tasks.id)
AND (smartmysql_tasks.status = 2)
AND (smartmysql_task_states.group_escalated = 0)
AND (smartmysql_tasks.deleted = 0)
AND (smartmysql_tasks.spam = 0)
AND (smartmysql_tasks.client_id = 178244)
AND (smartmysql_task_states.client_id = 178244)
AND (smartsql_groups.account_id = 178244 )
AND ((smartmysql_tasks.created_at + INTERVAL smartsql_groups.assign_time SECOND) <= '2017-11-07 02:58:25')
AND ISNULL(smartmysql_task_states.first_assigned_at)
AND (smartmysql_tasks.updated_at > '2017-09-07 02:58:25')
AND (smartsql_groups.id = smartmysql_tasks.group_id))
ORDER BY
smartmysql_tasks.id LIMIT 1000;Dynamic Query builder is another advanced feature and you can develop your SQL Queries 10X faster than MySQL Workbench.