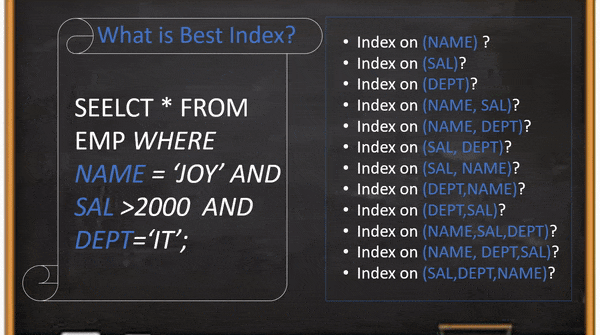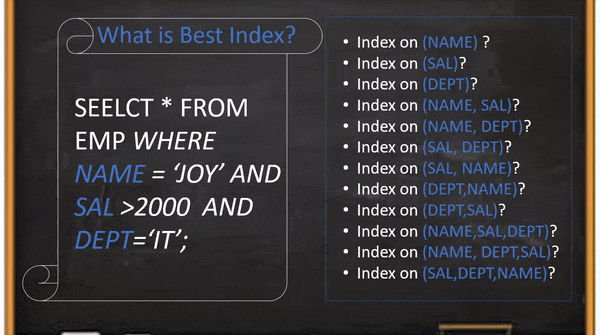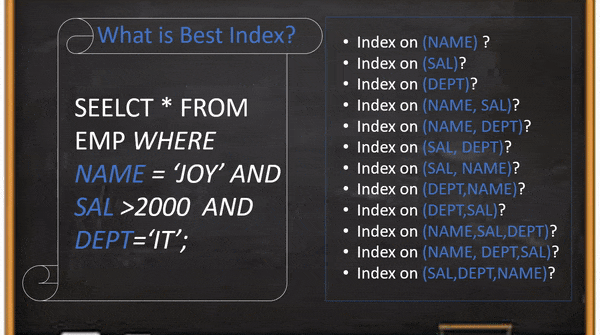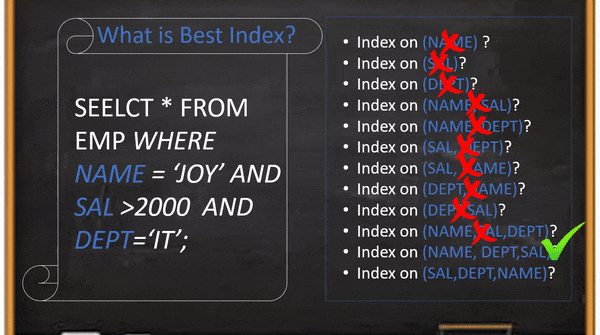
MySQL delete with join used to delete existing data from more than one table. In this blog, we explain a simple, easy and efficient way to write DELETE command even you no need to remember the syntax.
MySQL Delete Join Syntax
DELETE Table1, Table2
FROM Table1
INNER JOIN Table2 ON Table1.key = Table2.key
WHERE condition;If you want to delete only table1 data, in that case, need to remove table2 present in between delete, from clauses. If you want to delete only table2 data, in that case, need to remove table1 present in between delete, from clauses.
MySQL Delete Join Example
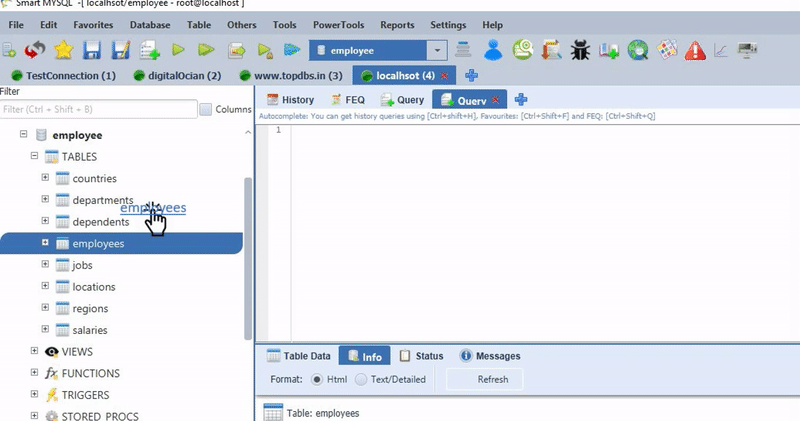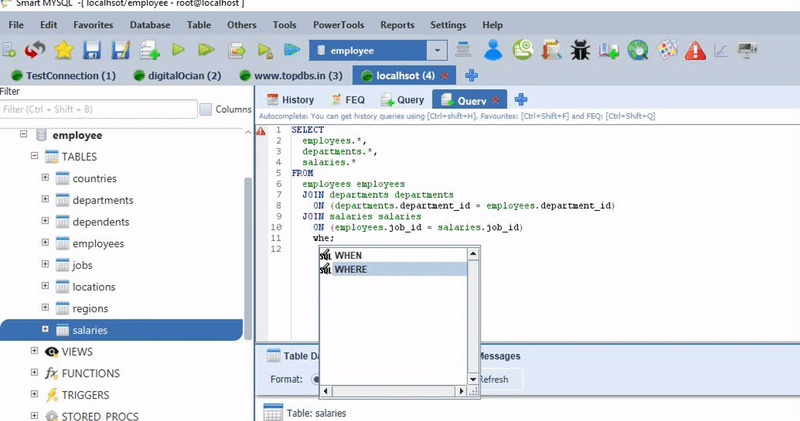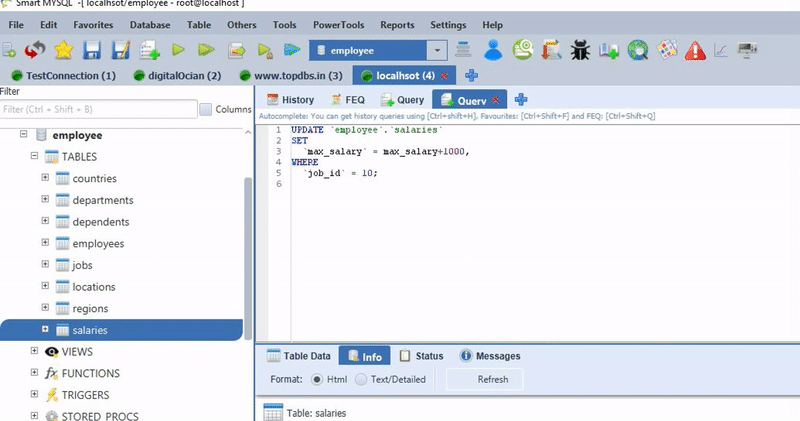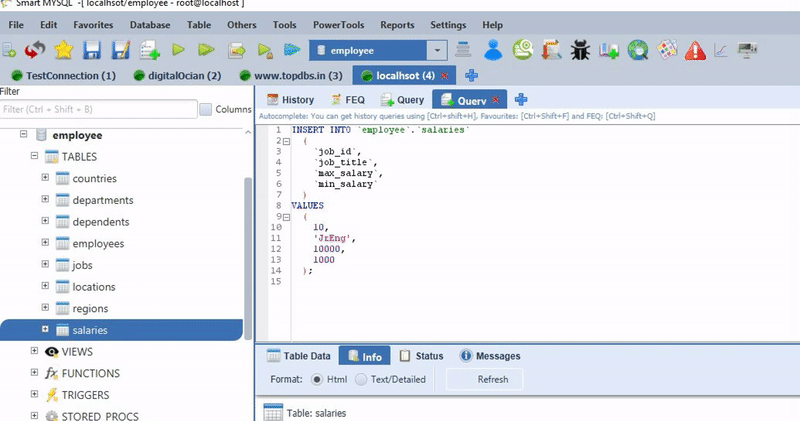
DELETE e.*,d.* FROM employee e
INNER JOIN departments d
ON (d.dept_no = e.dep_no)
WHERE
e.email = '';You can simply drag a table into the existing DELETE statement then it Reconstructs DELETE query with the table with JOIN condition. Ex: if I drag Department table then it generates the following DELETE command with JOIN condition.
You need to add d.* if you want to delete from the Department table. It is not possible to delete data from both tables using a single DELETE statement.
Ex: If I want to DELETE Employees who are working in the Marketing department and having more than 70 years old then in step 1 we need to drag birth_date column from the Employee table after D then we need to drag the Department table into the DELETE statement. It will generate the JOIN condition with the Department table. After we can add dept_name=’Marketing’ filter in the where clause and then also need to modify firth_date < curdate() – interval 70 years. we need to add e.* after DELETE.
DELETE e.* FROM employee e
INNER JOIN departments d
ON (d.dept_no = e.dep_no)
WHERE
e.hire_date < CURDATE() - INTERVAL 70 YEAR
and d.dept_name='Marketing';Please let us know there are any other ideas to simply DELETE query construction, we will consider your ideas and give rewards for your ideas.
The SmartMySQL Workbench is free and you can download. If any problem contacts support@smartmysql.com.