Update multiple columns with select query used to update multiple existed records with select query return rows.
Update Multiple Columns With A Select Syntax
UPDATE [LOW_PRIORITY] [IGNORE] table_reference
SET
column_name1=(select column_name from table_name where where_condition),
column_name2=(select column_name from table_name where where_condition),
.............
[WHERE where_condition]
[ORDER BY ...]
[LIMIT row_count]- After UPDATE Need to follow Table Name Ex: film_actor.
- SET clause: In the SET clause, we need to specify a list of columns that we need to change and assign new values by using select.
- Where clause: where the condition is useful for specifying which records need to update. If you forgot WHERE condition then it will update all records.
- Even you can specify ORDER BY and LIMIT in the MySQL update command. But if you are updating all records don’t specify ORDER BY for best practice.
- You can use LOW-PRIORITY, it will wait until other high priority threads that are using the same resource.
- If you use IGNORE then it will not return an error in case of Primary key or UNIQUE key violation.
Update Multiple Columns With Select Example
UPDATE `smartmysql_testing`.`film_actor` fa
SET
fa.actor_id = (SELECT `actor_id` FROM actor a),
fa.last_update = (SELECT last_update FROM actor a)
WHERE
fa.actor_id = 'actor_id';SmartMySQL Workbench has advance options for writing UPDATE command and you no need to remember UPDATE command syntax.
If you Type U or UPDATE then drag table after U letter or UPDATE Keyword then it generates UPDATE COMMAND for that table. Ex: if you type U then drag the “film_actor” table then it generates the following UPDATE command.
UPDATE `smartmysql_testing`.`film_actor` fa
SET
fa.actor_id = 'actor_id',
fa.last_update = 'last_update'
WHERE
fa.actor_id = 'actor_id';if U drag table name inside braces after column name it will give the select query (or) drag table after select keyword will give select query.
UPDATE `smartmysql_testing`.`film_actor` fa
SET
fa.actor_id = (SELECT `actor_id` FROM actor a),
fa.last_update = (SELECT last_update FROM actor a)
WHERE
fa.actor_id = 'actor_id';Default it will get all columns where SET Clause. You can keep which column you need rest you can remove. By default, it will generate where condition with the primary key column. If you need other columns in WHERE clause then you need to drag the column after U letter.
MySQL UPDATE with JOIN
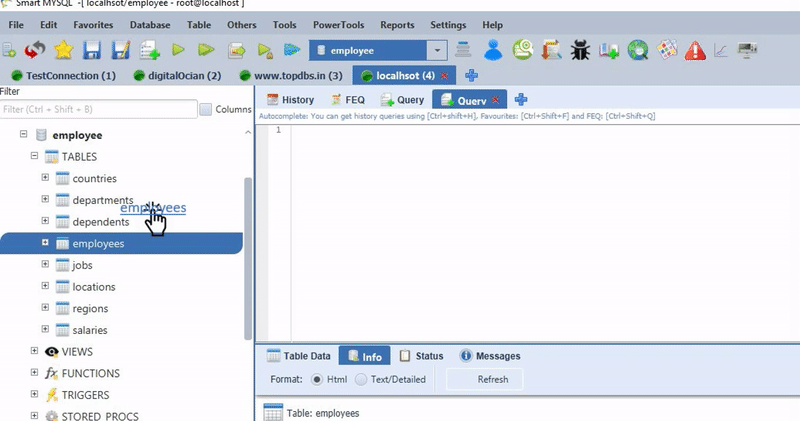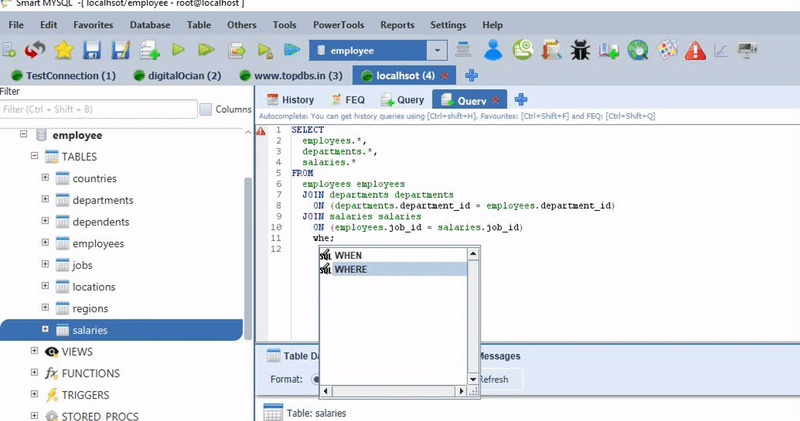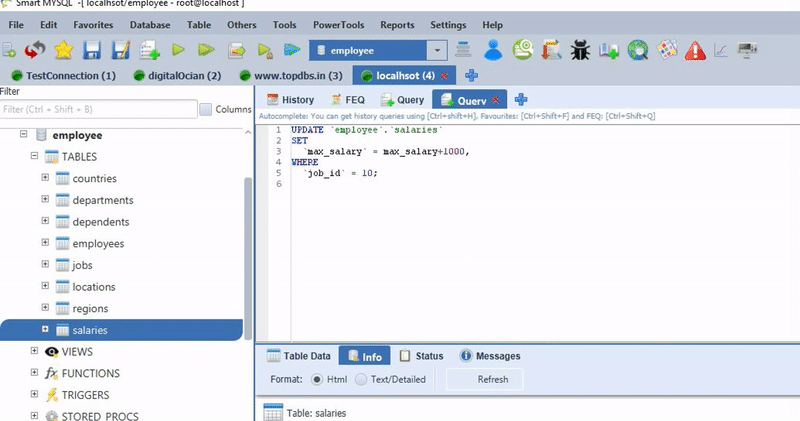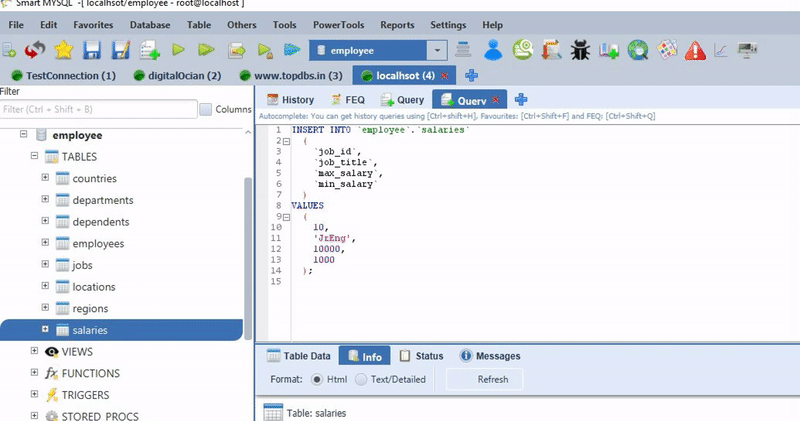
You can simply drag a table into the existing UPDATE statement then it generates UPDATE query with the table with joins condition. Ex: if I drag Department table then it generates the following UPDATE command with JOIN condition.
UPDATE employee e
INNER JOIN departments d
ON (d.dept_no = e.dep_no)
SET
e.emp_no = 'emp_no',
e.birth_date = 'birth_date',
e.first_name = 'first_name',
e.last_name = 'last_name',
e.gender = 'gender',
e.hire_date = 'hire_date',
e.email = 'email',
e.dep_no = 'dep_no',
e.salary = 'salary'
WHERE
e.email = '';This option is available in SmartMySQL free version and if you use SmartMySQL you no need to remember any syntax. You just remove an unwanted column in the SET clause and fill values in the WHERE condition.
Ex: If I want to increase salary 10% for the Marketing department then I just keep the salary column in the SET clause in the above column and add dept_name in where clause and fill filter condition like dept_name=’Marketing’.
UPDATE employee e
INNER JOIN departments d
ON (d.dept_no = e.dep_no)
SET
e.salary = salary*110/100
WHERE
dept_name='Marketing';Please let us know there are any other ideas to simply UPDATE query construction, we will consider your ideas and give rewards for your ideas.
The SmartMySQL Workbench is free and you can download. If any problem contacts support@smartmysql.com.